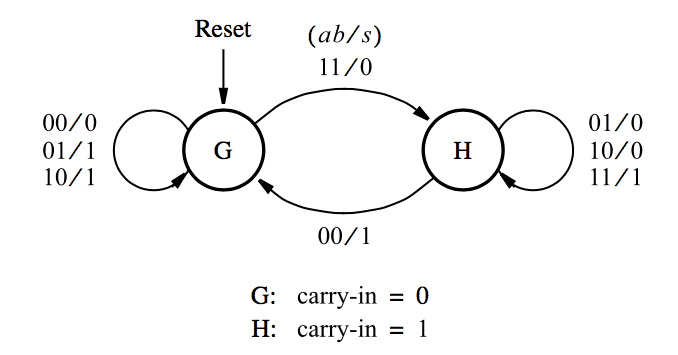
- Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Design
- Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Diagram
4.2.8 Incomplete VHDL/SystemVerilog Code 76 4.2.9 Overregistered VHDL/SystemVerilog Code 78 4.3 Design Steps Summary 79 5 Regular (Category 1) State Machines 81 5.1 Introduction 81 5.2 Architectures for Regular (Category 1) Machines 82 5.3 Number of Flip-Flops 84 5.4 Examples of Regular (Category 1) Machines 84. A finite-state machine (FSM) or simply a state machine is used to design both computer programs and sequential logic circuits. It is conceived as an abstract machine that can be in one of a finite number of user-defined states. The machine is in only one state at a time; the state it is in at any given time is called the current state. Wall mount for mac. Finite state machines — FPGA designs with VHDL documentation. Finite state machines ¶. In previous chapters, we saw various examples of the combinational circuits and sequential circuits. In combinational circuits, the output depends on the current values of inputs only; whereas in sequential circuits, the output.
Finite state machine is a graphical model/representation of sequential activities or events. After representing and modeling the events they can be implemented easily in case of sequential logic designs. Finite state machines can be utilized in many fields of study e.g neural networks, artificial intelligence, mathematics, games, robotics and sequential flow of data. Since we are dealing with the sequential circuits so i will explain their use in sequential circuit design in this tutorial. |
- Melay Machine
- Moore Machine
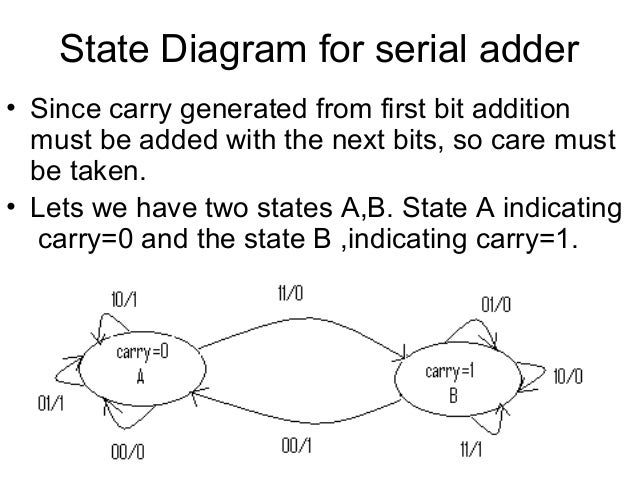
Moore Machine
- More number of states in moore compared to melay for same fsm.
- States changes after 1 clock cycle. Latency = 1.
- Synchronous output. Because the states are determined in a process.
- States are output.
Mealy Machine
- Less number of states in mealy compared to moore for same fsm.
- State transition on the same clock cycle. Latency = 0.
- Asynchronous output.
- Transition are output.

Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Design
Filed Under: Microcontroller Projects, VHDL
Moore Machine
- More number of states in moore compared to melay for same fsm.
- States changes after 1 clock cycle. Latency = 1.
- Synchronous output. Because the states are determined in a process.
- States are output.
Mealy Machine
- Less number of states in mealy compared to moore for same fsm.
- State transition on the same clock cycle. Latency = 0.
- Asynchronous output.
- Transition are output.
